Important things to understand in the fighting game genre for this project are :
KEYFRAMES
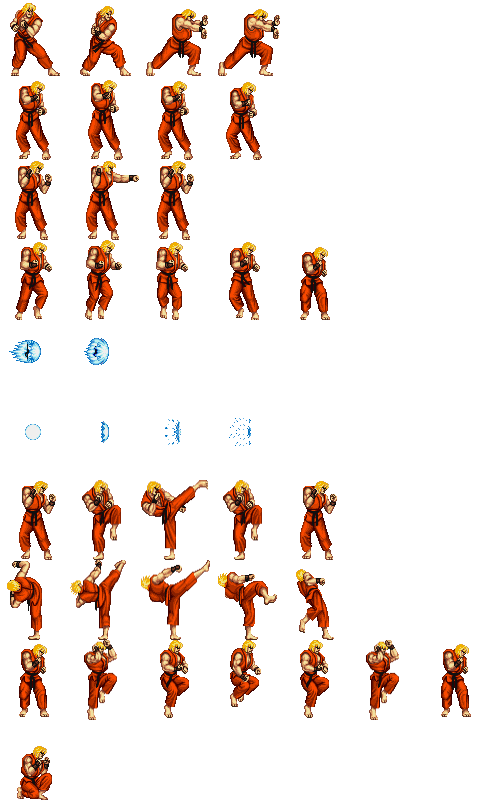
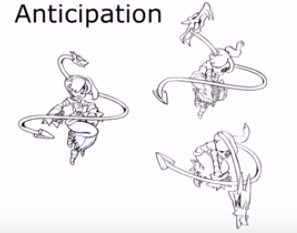
Fighting games are in essence nothing but interactive animations so that being said one of the most important aspects of them are the keyframes. However the main thing to focus on when animating in 2D fighters is creating strong key-poses that show the specific move distinctly so that players can act and react accordingly.

It is also important to consider the 12 basic principles of animation when creating fighting games in order to give each motion a dynamic look and feel. Thing such as –
Exaggeration
Anticipation
And Followthrough
These are all important factors that show the power behind each move and gives each character a more unique personality.
ARCHETYPES
In fighting games there are generally character archetypes that appear in every game that allow for a wide variety of playstyles in each individual game. These include but are not limited to :
Zoners

Typically projectile based characters, zoners focus on keeping distance between themselves and the opponent by utalising projectile or long range attacks that allow them to deal damage from across the screen.
Rushdown

Rushdown character focus on using their speed to get up close to their oponent. They are normally good at creating combos and keeping up the pressure on their oponent.
Grappler
Grapplers are almost entirely focused on using their strength to overwhelm the oponent by using grappling and throws which will often stun and deal large amounts of damage with a downside of being slower than most other archetypes
Counter

Counter characters are heavily built around the use of parrys and counters to create a defensive playstyle that allows them to deal damage without risking themselves as mush as well as being able to start combos in a defensive manner.
Taunt

Taunt characters are often considered comic relief however in many games the taunts utilised can be used as a distracton from what moves they are going to use next to make them more unpredictable fighters
CHARACTER DESIGN
In fighting games perhaps the most important aspect is the character design as when most people begin playing the first character they will pick will be based on what appeals to them. When designing a character you must focus on many different aspects such as –
Their personality

Johnny cage from mortal kombat is characterised as an egotistical hollywood action hero and you can see this from the way he has his own name tattooed on him, the blacked out shades he wears, His van Damme inspired hair and his arm wraps typically used by stereotypically bad ass martial artists
The way they fight

Baek Doo San from Tekken is a traditional practitioner of taekwondo and that is clearly shown by the fact he wears his dobok (Taekwondo fighting outfit) In game
Their background

Laura from street fighter 5 is an outgoing and energetiv character who originates from brazil which is represented in her modified jujisu gi that is in the in her countries colours.
LEVEL BACKGROUNDS
Levels in 2d fighting games are important for building on the story and giving a unique feel to each fight despite the fact that from a gameplay perspective they are often exactly the same. Each level can show character and personality while also not distracting from the fight itself.